Operating Systems Theory and Designs Final Project
Describe features of contemporary operating systems and their structures.
There are three major players for contemporary Operating System these are the most popular OS out in the market. The BIG Three includes Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. Microsoft Windows covers a substantial margin of market share in both laptop and desktop markets, while the server and embedded device markets are split amongst several OSs. A structure of an Operating System regulates in what way it has been constructed and how it operates. There are several approaches of designing a new configuration of an Operating system. There are six sequences that have been tested. These six combinations are monolithic systems, layered systems, microkernels, client-server models, virtual machines, and exokernels.
Monolithic System structure in an Operating System
In this organizational structure, the entire operating system runs as a single program in the kernel mode. An operating system is a collection of various procedures linked together in a binary file. In this system, any procedure can call any other procedure. Since it is running in kernel mode itself, it has all the permissions to call whatever it wants.
Layered Systems Structure in Operating Systems
As the name suggests, this system works in layers. It was designed by E.W. Dijkstra in 1968, along with some help from his students. This system was first implemented in THE system built at the Technische Hogeschool Eindhoven in the Netherlands. The THE system was a simple batch system for a Dutch computer, the Extralogica X8.
Microkernels system in an operating system
Traditionally, all the layers of the OS in a layered system went into the kernel. So they all had root access to the OS, and any small bug in any layer could be fatal to the OS.
Client-Server Model in Operating Systems
The client-server model in an operating system is a variation of the microkernel system. The middle layer in the microkernel system is the one with servers. These servers provide some kind of service to clients. This makes up the client-server model.
Virtual Machines in Operating systems
When many users wanted to work interactively in terminals, IBM started working on a time-sharing system. The idea of a virtual machine is straightforward. The virtual machine is run on the hardware of the OS it is being installed. A virtual machine thinks it has its own disk, with blocks running from 0 to some maximum, so the virtual machine monitor must maintain tables to remap disk addresses and all other resources.
Exokernels
Exokernels are a subset of virtual machines. In this, the disks are actually partitioned, and resources are allocated while setting it up. The different OS may be installed on different partitions. Beneath both, the partition is what we call the exokernel.
Discuss how operating systems enable processes to share and exchange information.
The OS must allocate resources that enable processes to share and exchange information. It also protects the resources of each process from other methods and allows synchronization among processes. It is the job of OS to manage all the running processes of the system
Explain how main memory and virtual memory can solve memory management issues.
Virtual memory can be used to swap data that has not been used recently – and move it over to a storage device like a hard drive or solid-state drive (SDD). This will free up more space on the RAM. Virtual memory is important for improving system performance, multitasking, using large programs and flexibility.
Explain how files, mass storage, and I/O are handled in a modern computer system.
A SD card. Hard drives are amongst the most common types of mass storage devices. Most computers have a hard disk drive already built into them, and they can offer a large amount of memory which can be accessed easily by the user.
Outline the mechanisms necessary to control the access of programs or users to the resources defined by a computer system.
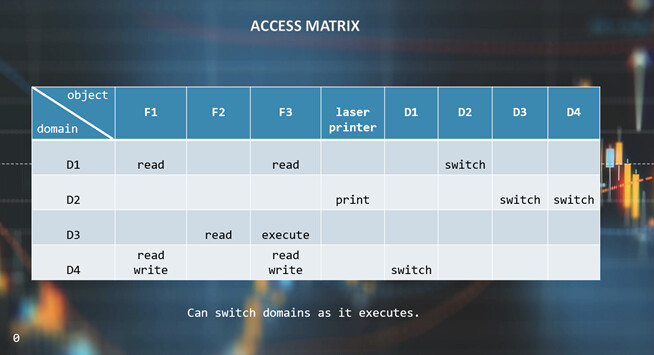
Protection refers to a mechanism for controlling the access of programs, processes, or users to the resources defined by a computer system. There are many different hardware and software systems within a computer that require protection. A general model of protection for a system can be viewed as an Access Matrix.
Recommend how you will use these concepts about operating systems theory in future courses and/or future jobs.
In Summary, my biggest take away in this class is the overall concept of the operating system and how it works. It is fascinating to unfold information and various data how to different OS work and its functionality. One of function I can use in my day to day is the memory allocation. It helped me understand in depth how it calculates and allocate commands. It will aid my study in future classes on how to utilize and configure data based on requirements. This class is vital when on someone that is aspiring and pursuing a career in computer architecture. This class is going to enlightened you what are the steps needed to create concept map on in order to improve the reliability and consistency of the system being used in an organization.
[“source=discuss.folio”]